Abstract
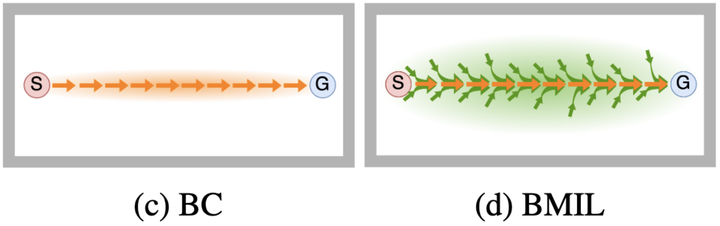
Behavior cloning of expert demonstrations can speed up learning optimal policies in a more sample-efficient way over reinforcement learning. However, the policy cannot extrapolate well to unseen states outside of the demonstration data, creating covariate shift (agent drifting away from demonstrations) and compounding errors. In this work, we tackle this issue by extending the region of attraction around the demonstrations so that the agent can learn how to get back onto the demonstrated trajectories if it veers off-course. We train a generative backward dynamics model and generate short imagined trajectories from states in the demonstrations. By imitating both demonstrations and these model rollouts, the agent learns both the demonstrated paths and how to get back on to these paths. With optimal or near-optimal demonstrations, the learned policy will be both optimal and robust to deviations, with a wider region of attraction. On continuous control domains, we evaluate the robustness when starting from different initial states unseen in the demonstration data. While both our method and other imitation learning baselines can successfully solve the tasks for initial states in the training distribution, our method exhibits considerably more robustness to different initial states.